I weigh in on Google Glass at KCET.
The gist:
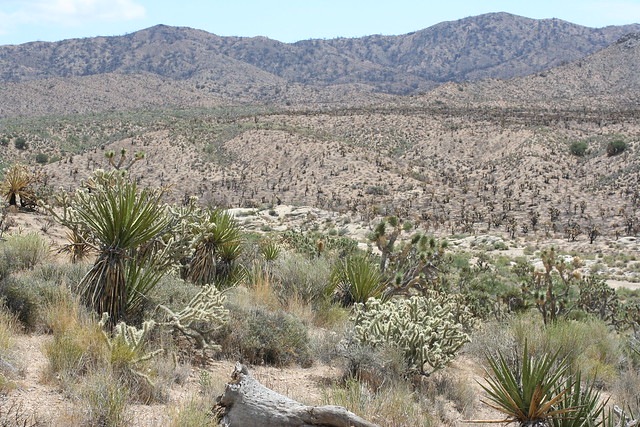
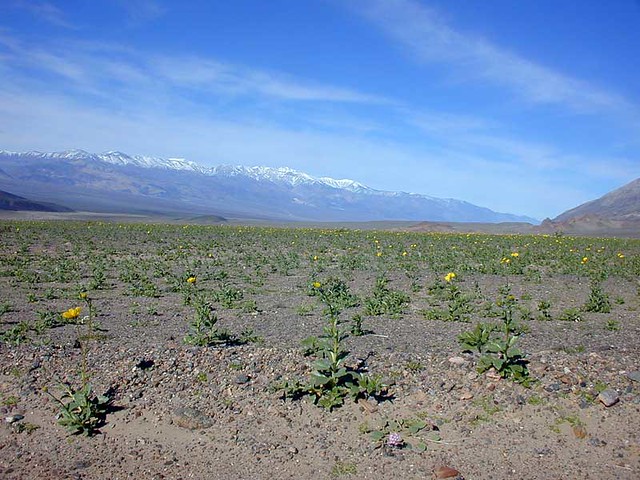
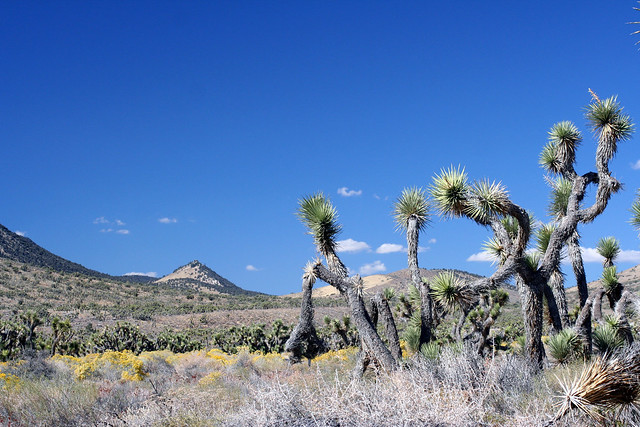
Some of us come out to the desert to escape the Panopticon that life in the city already is, increasingly. In Los Angeles, Google Glass might be just one more increment of invasion in a landscape already thoroughly colonized by surveillance cameras, red light cameras, random private webcams, smart phone videographers and other such prying eyes. But there are places out here that don’t even have 4G yet. In fact — and you might want to sit down here and swallow that mouthful of coffee — there are some places out here where even the 3G coverage is spotty. We are in the back of beyond here in much of Eastern California.
And we like it that way, mostly.
So by all means, come on out and visit the desert. Bring your recording equipment, whether it’s a shoulder-mounted Steadicam or this latest bit of geek lust from Google sitting on your face. Document your hike. Record that coyote begging for sandwiches. Take video of that gorgeous desert bloom backlit by sunrise. The desert needs all the documentation it can get.
But if you’re talking to me, take that Google Glass off and put it away. If I’m speaking in public — which I do from time to time, offering lectures and poetry readings and such — and see you’re in my audience wearing Google Glass and you haven’t cleared it with me first, I will stop what I’m doing and ask you to put it away or leave. If you’re at an adjacent cafe table facing me and recording in my direction, I will write something derogatory in Sharpie on a sheet of paper and hold it up. I may escalate from there. And I’m not alone.