I remember the Olden Times when Rush Limbaugh (may he Rot in Peace) would rail against solar power — what will we do when the sun goes down? — and wind power — what about calm days? — and tell us to keep burning coal and gas.
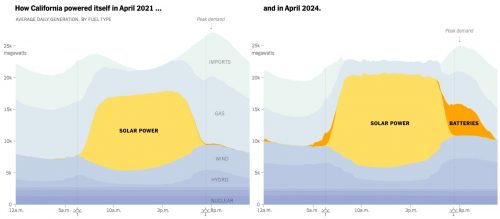
Technology marches forward, and now we have these things called batteries that can smooth out the highs and lows of electricity production. Now when we hear about solar farms going up, they’re usually accompanied by energy storage farms. Here’s what energy production in California looks like:
Solar power production is swelling during the day, and is extended into the peak demand period with batteries. Maybe they could also expand wind power, and possibly be better at conserving energy? I think if I plotted energy usage at my house, it would be much more uniform: we don’t have air conditioning, and I’ve done more cooking with an eye towards preparing meals that can produce leftovers that last a few days.
As it is, California is sometimes producing more solar energy than it can use. They have to throttle solar power output back, or even pay neighboring states to take it.
Good things are happening here in Minnesota, too. We’ve got a gigantic energy storage facility going up in Becker, a town between Morris and the Twin Cities.
One of the largest solar projects in the country is moving closer to completion, and it’s not in a famously sunny state like California, Texas, or even Florida. It’s in Minnesota, on former potato farms near the site of a retiring coal plant.
The Sherco solar and energy-storage facility will be the largest solar project in the Upper Midwest, and the fifth-largest in the U.S. by the time it’s fully completed in 2026. The first phase of the project should begin sending emissions-free electricity to the grid this fall, heralding the start of a new era in a state whose largest solar project until now has been just 100 megawatts. This new project will have a capacity of 710 megawatts. It’s being built by utility Xcel Energy, which will also operate the facility once it’s online.
The project is poised to deliver on the many promises of renewable energy: It will partially replace the nearby coal plant set to retire over the coming years, address the variability of solar power by pairing it with long-duration storage, and provide good-paying union jobs in a community that’s losing a key employer in the coal facility.
They’re using iron-air batteries, which are cheaper and less toxic and less flammable than the now-familiar lithium batteries. It’s also positive that this facility is going up explicitly to replace a coal plant, one we often saw as we drove along I-94. It hasn’t been so prominent in recent years, I guess they’ve been gradually shutting it down and we don’t see the giant exhaust plumes so much any more.
Even closer to home, my university has begun a major energy storage project.
For many years now, UMN Morris and UMN WCROC [West Central Research and Outreach Center], have explored the potential of energy storage in rural Minnesota.
Now, UMN Morris and UMN WCROC are partnering to launch the Center for Renewable Energy Storage Technology, or CREST. In order to reach high levels of renewable power generation, efficient and economic energy storage systems are critically needed. This field is poised for significant growth and attention in the coming years. The new UMN intercollegiate Center will provide leadership in research, demonstration, education, and outreach in this vital field by organizing teams and partnerships and incubating energy storage research and demonstration-scale projects.
A hallmark and unique characteristic of renewable energy efforts at the Morris campuses has been the ability to test systems at commercial or near-commercial scales. This scale is especially crucial in moving new technologies from labs into the commercial market. CREST will also expand opportunities for Minnesotans to learn more about energy storage technologies and potential applications. Recently, UMN WCROC announced it will host the $18.6 million US DOE ARPA-E REFUEL Technology Integration 1 metric ton per day ammonia pilot plant. In addition, WCROC received $10 million from the State of Minnesota in the 2021 legislative session through the Xcel Energy RDA account to develop ammonia-fueled power generation and self-contained ammonia storage technologies. UMN Morris announced a new project to develop a large-scale battery-storage demonstration project. These projects are done in collaboration with partners from across the University of Minnesota and with many partners in the public and private sectors.
It’s too bad we can’t rub Limbaugh’s face in the progress that’s being made.