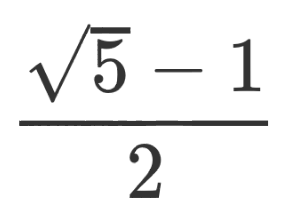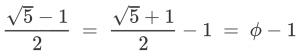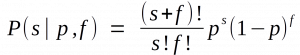You remember them, right? A secretive group within the FBI who targeted “domestic subversives” like Martin Luther King Jr. and Roberta Salper, with tactics that ranged from surveillance to blackmail to false flag ops and entrapment. Even the modern FBI agrees it was both unethical and unlawful.
Rakem Balogun thought he was dreaming when armed agents in tactical gear stormed his apartment. Startled awake by a large crash and officers screaming commands, he soon realized his nightmare was real, and he and his 15-year-old son were forced outside of their Dallas home, wearing only underwear.
Handcuffed and shaking in the cold wind, Balogun thought a misunderstanding must have led the FBI to his door on 12 December 2017. The father of three said he was shocked to later learn that agents investigating “domestic terrorism” had been monitoring him for years and were arresting him that day in part because of his Facebook posts criticizing police.
This isn’t on the same level, but it’s close. FBI officials monitored, arrested, and prosecuted Rakem Balogun for the high crime of being angry enough at how black people are treated in the USA to organize and agitate.
Authorities have not publicly labeled Balogun a BIE [Black Identity Extremist], but their language in court resembled the warnings in the FBI’s file. German said the case also appeared to utilize a “disruption strategy” in which the FBI targets lower-level arrests and charges to interfere with suspects’ lives as the agency struggles to build terrorism cases.
“Sometimes when you couldn’t prove somebody was a terrorist, it’s because they weren’t a terrorist,” he said, adding that prosecutors’ argument that Balogun was too dangerous to be released on bail was “astonishing”. “It seems this effort was designed to punish him for his political activity rather than actually solve any sort of security issue.”
The official one-count indictment against Balogun was illegal firearm possession, with prosecutors alleging he was prohibited from owning a gun due to a 2007 misdemeanor domestic assault case in Tennessee. But this month, a judge rejected the charge, saying the firearms law did not apply.
Ruined his life for it, too; he lost his job, house, and car because of overzealous FBI agents. Amazingly, their crusade lacks the weight of evidence.
The government’s own crime data has largely undermined the notion of a growing threat from a “black identity extremist” [BIE] movement, a term invented by law enforcement. In addition to an overall decline in police deaths, most individuals who shoot and kill officers are white men, and white supremacists have been responsible for nearly 75% of deadly extremist attacks since 2001.
The BIE surveillance and failed prosecution of Balogun, first reported by Foreign Policy, have drawn comparisons to the government’s discredited efforts to monitor and disrupt activists during the civil rights movement, particularly the FBI counterintelligence program called Cointelpro, which targeted Martin Luther King Jr, the NAACP and the Black Panther party.
OK, if I keep talking about this I’ll just wind up quoting the entire article. Go read it and witness the injustice yourself.