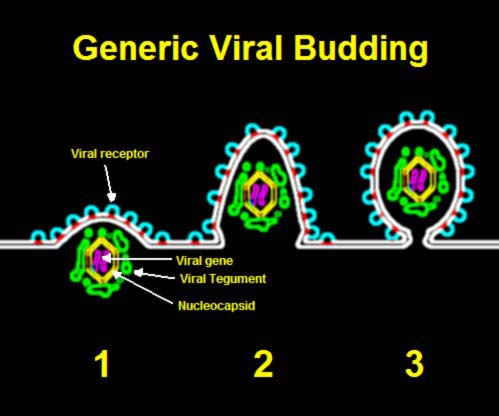
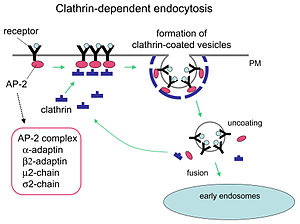
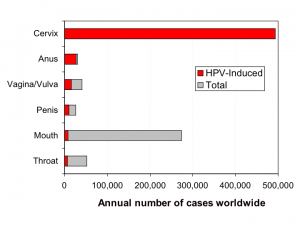
You might think I’m writing a check with that headline these blogg’n finger can’t cash. If so, you would be wrong! There really is such a report out and vaginas are not the only things being grown in vitro, or outside of the body, whatever the terminology might be. [Read more…]